Crafting the Digital Experience: An Introduction to Frontend Development
In today’s tech-driven world, the first impression of any website or app often determines its success. That first impression? It’s all thanks to frontend development. Whether you’re an aspiring developer or a tech enthusiast, understanding frontend development reveals how engaging digital experiences come to life.
What is Frontend Development?
Frontend development focuses on the user-facing part of web applications—the visual elements you see and interact with in your browser. It bridges the gap between design and functionality, ensuring that websites are both beautiful and user-friendly.
Core Components of Frontend Development
HTML (HyperText Markup Language):
The backbone of any web page, HTML structures the content. It defines elements like headings, paragraphs, and links.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets):
CSS brings HTML to life with styles, colors, layouts, and animations. Modern frameworks like Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap simplify responsive design.
JavaScript:
This programming language adds interactivity, making web pages dynamic. Think of dropdown menus, form validations, and interactive maps—all powered by JavaScript. Libraries and frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Angular enhance JavaScript's capabilities.
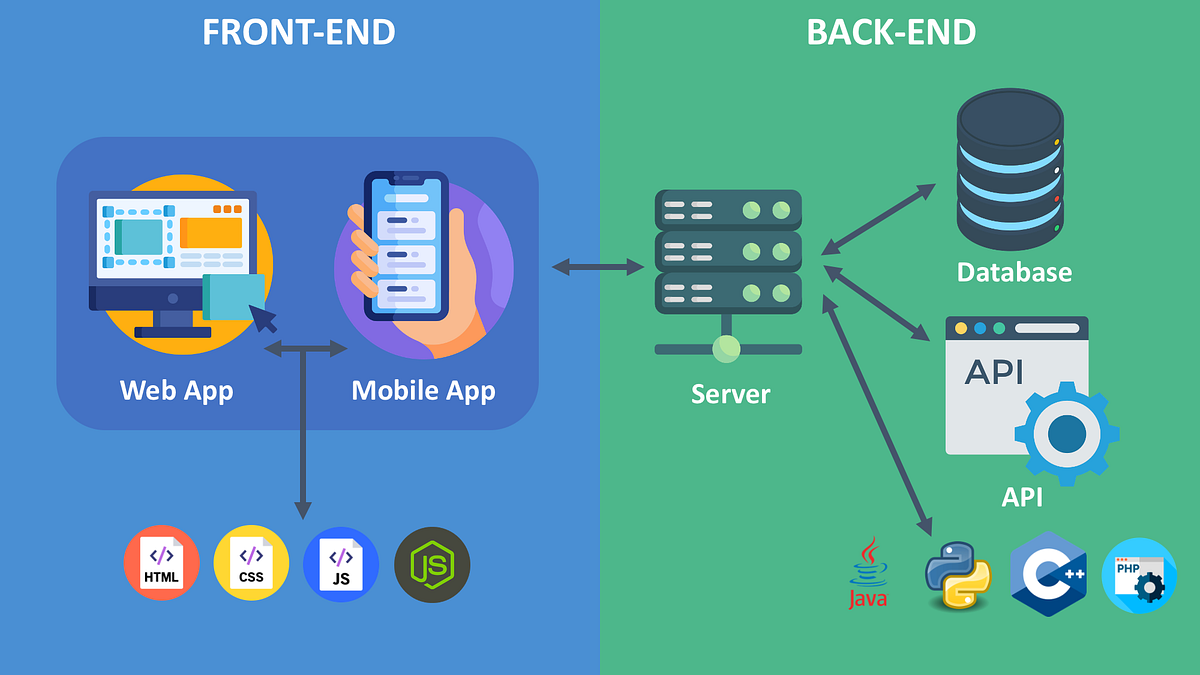
How Frontend and Backend Collaborate
When you interact with a web application, the frontend sends requests to the backend (like submitting a login form). The backend processes the data and sends a response, which the frontend then displays. This seamless interaction creates a smooth user experience.
Challenges in Frontend Development
Backend development refers to the server-side portion of an application. It involves everything that happens behind the scenes—database interactions, server logic, and API integration. While the frontend focuses on what users see and interact with, the backend ensures that data is processed securely and efficiently.
Cross-Browser Compatibility:
Ensuring a site looks and functions consistently across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) requires careful testing and coding.
Responsive Design:
With users accessing websites from various devices, responsive design ensures a consistent experience on phones, tablets, and desktops.
Performance Optimization:
Fast load times are crucial. Techniques like lazy loading, image optimization, and minimizing CSS/JavaScript files improve performance.
Tools Every Frontend Developer Should Know
- Code Editors: VS Code, Sublime Text, and Atom enhance productivity.
- Version Control: Git tracks changes and facilitates collaboration.
- Frontend Frameworks: React, Angular, and Vue.js streamline complex projects.
- Build Tools: Webpack and Vite bundle code and optimize assets.
- Testing Tools: Jest and Cypress ensure reliable and bug-free applications.
